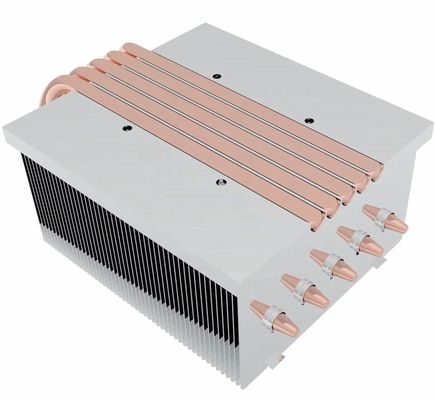
Few experiences are as frustrating as a laptop that suddenly crashes or slows to a crawl. Often, the culprit is overheating – a silent efficiency killer that can damage hardware and disrupt productivity. Your laptop's cooling system, particularly its heat sink, serves as an unsung guardian, swiftly dissipating the intense heat generated by the central processing unit (CPU) to prevent performance throttling and permanent component damage.
Much like an engine without coolant, a laptop without proper thermal management faces catastrophic consequences. Understanding how cooling systems work and recognizing early warning signs can save both your device and your workflow.
The Science Behind Laptop Cooling
Heat sinks operate on simple thermodynamic principles. When the CPU generates heat, thermal compounds (typically thermal paste or pads) transfer this energy to metal fins – usually made of aluminum or copper – which maximize surface area for heat dissipation. Active cooling systems enhance this process with fans that force air circulation, while high-performance laptops often require advanced cooling solutions to handle intensive computational tasks.
However, cooling systems require maintenance. Dust accumulation impedes airflow, reducing efficiency. Regular cleaning with compressed air prevents this degradation. Warning signs like unexpected shutdowns, abnormal surface temperatures, or performance drops indicate cooling issues that demand immediate attention.
Recognizing Overheating Symptoms
1. Sudden Shutdowns
When cooling systems fail, emergency thermal protection forces immediate shutdowns to prevent hardware damage. These abrupt power-offs risk data loss and workflow interruption.
2. Performance Throttling
Noticeable slowdowns during resource-intensive tasks signal thermal throttling – when systems reduce CPU/GPU speeds to lower temperatures, sacrificing performance for safety.
3. Excessive Fan Noise
Persistent loud fan operation indicates cooling systems working overtime to compensate for inadequate heat dissipation, often due to clogged vents or degraded thermal paste.
4. System Crashes
Overheating destabilizes components, causing unpredictable freezes or application crashes that disrupt productivity and risk unsaved work.
5. Surface Heat
Excessive external warmth near CPU/GPU areas suggests internal heat isn't being properly dissipated, potentially harming components and user comfort.
6. Temperature Alerts
Built-in monitoring tools that frequently warn of unsafe operating temperatures clearly indicate cooling system deficiencies.
Essential Repair Tools
-
Precision screwdrivers:
For handling delicate laptop screws
-
Plastic pry tools:
To safely open casings without scratches
-
High-quality thermal paste:
For optimal heat transfer between CPU and heat sink
-
Isopropyl alcohol (90%+):
For cleaning old thermal compounds
-
Anti-static wristband:
To prevent electrostatic discharge damage
-
Compressed air:
For dust removal from vents and fans
-
Replacement parts:
Heat sinks or thermal pads when necessary
Step-by-Step Cooling System Maintenance
-
Prepare workspace:
Clean, well-lit area with all tools accessible
-
Disassemble laptop:
Power off, remove battery, carefully open casing
-
Clean components:
Remove dust with compressed air, clean old paste with alcohol
-
Apply new thermal paste:
Pea-sized amount spread evenly across CPU
-
Reassemble:
Secure heat sink, reattach casing components
Preventative Maintenance Strategies
-
Biannual cleaning of vents and fans
-
Using laptop stands for improved airflow
-
Monitoring temperatures with software like HWMonitor
-
Replacing thermal paste every 1-2 years
-
Keeping firmware updated for cooling optimizations
-
Avoiding use in hot/dusty environments
-
Annual professional servicing for thorough maintenance
Effective thermal management isn't merely about fixing immediate issues – it's an ongoing practice that preserves your laptop's health and functionality. Through consistent care and timely interventions, users can maintain optimal performance while avoiding the productivity pitfalls of overheating.

 Uw bericht moet tussen de 20-3.000 tekens bevatten!
Uw bericht moet tussen de 20-3.000 tekens bevatten! Controleer uw e-mail!
Controleer uw e-mail!  Uw bericht moet tussen de 20-3.000 tekens bevatten!
Uw bericht moet tussen de 20-3.000 tekens bevatten! Controleer uw e-mail!
Controleer uw e-mail!